Abstract
Domain adaptation enables the learner to safely generalize into novel environments by mitigating domain shifts across distributions. Previous works may not effectively uncover the underlying reasons that would lead to the drastic model degradation on the target task. In this paper, we empirically reveal that the erratic discrimination of the target domain mainly stems from its much smaller feature norms with respect to that of the source domain. To this end, we propose a novel parameter-free Adaptive Feature Norm approach. We demonstrate that progressively adapting the feature norms of the two domains to a large range of values can result in significant transfer gains, implying that those task-specific features with larger norms are more transferable. Our method successfully unifies the computation of both standard and partial domain adaptation with more robustness against the negative transfer issue. Without bells and whistles but a few lines of code, our method substantially lifts the performance on the target task and exceeds state-of-the-arts by a large margin (11.5% on OfficeHome and 17.1% on VisDA2017). We hope our simple yet effective approach will shed some light on the future research of transfer learning. Code is available at https://github.com/jihanyang/AFN.
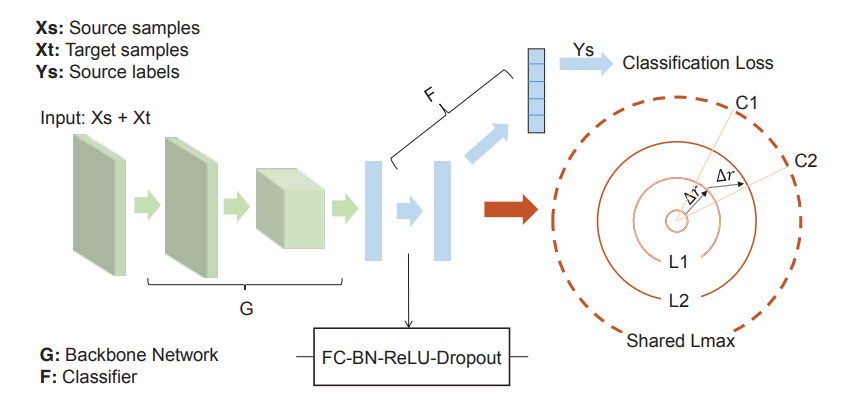
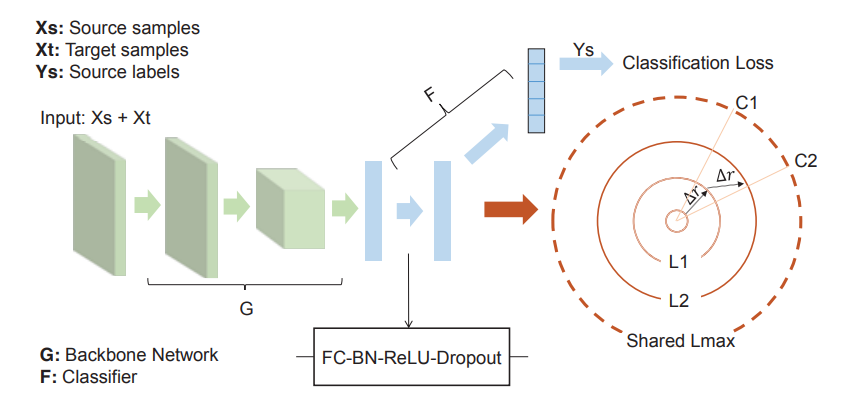
Framework
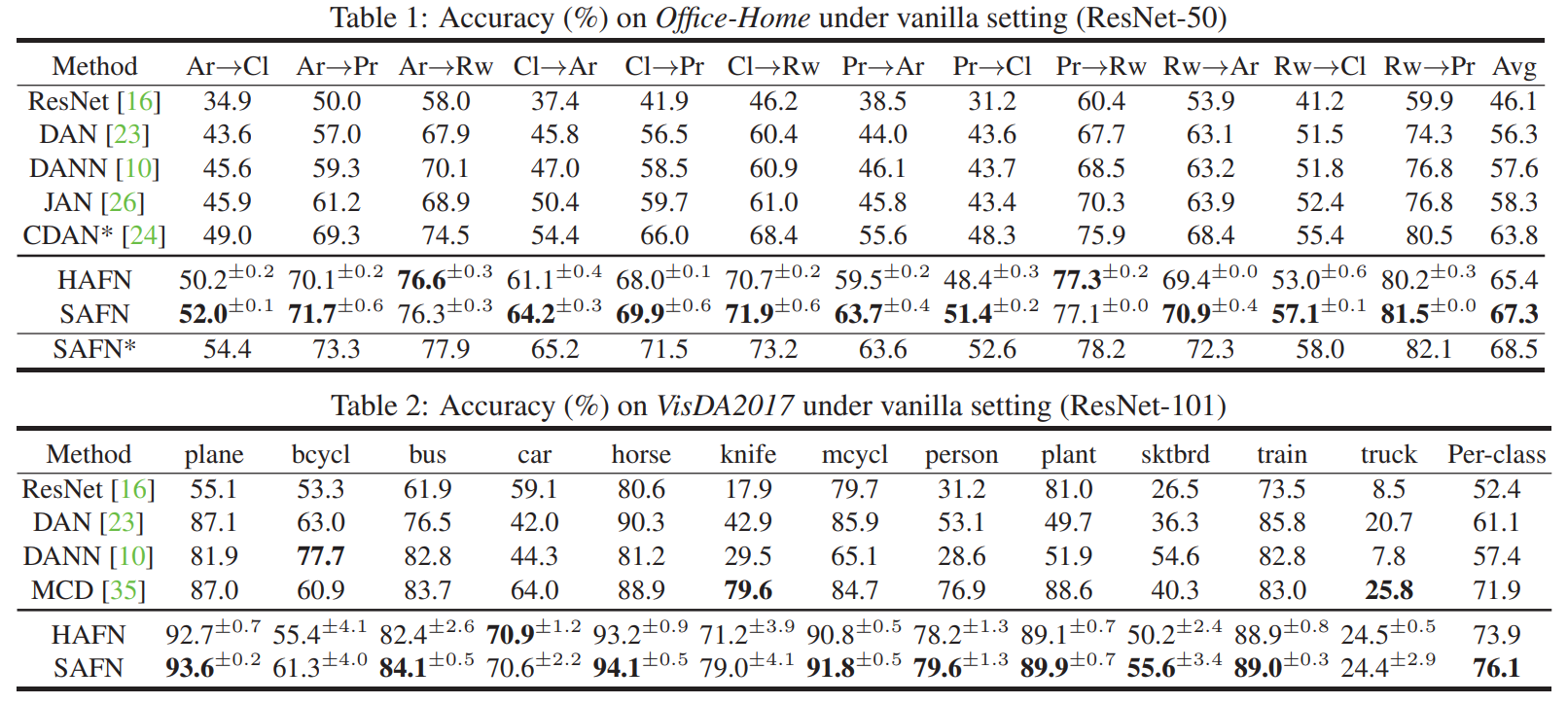
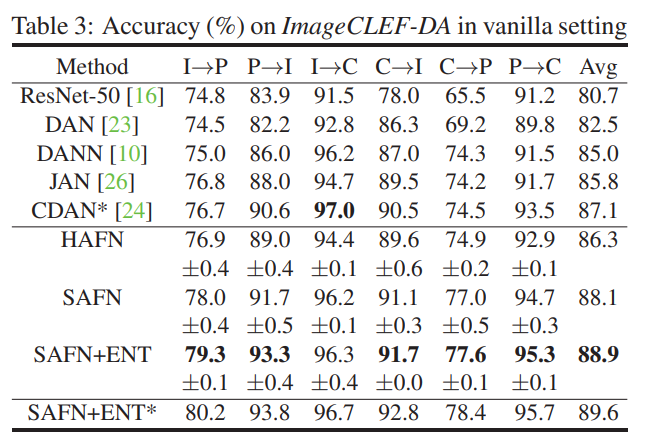
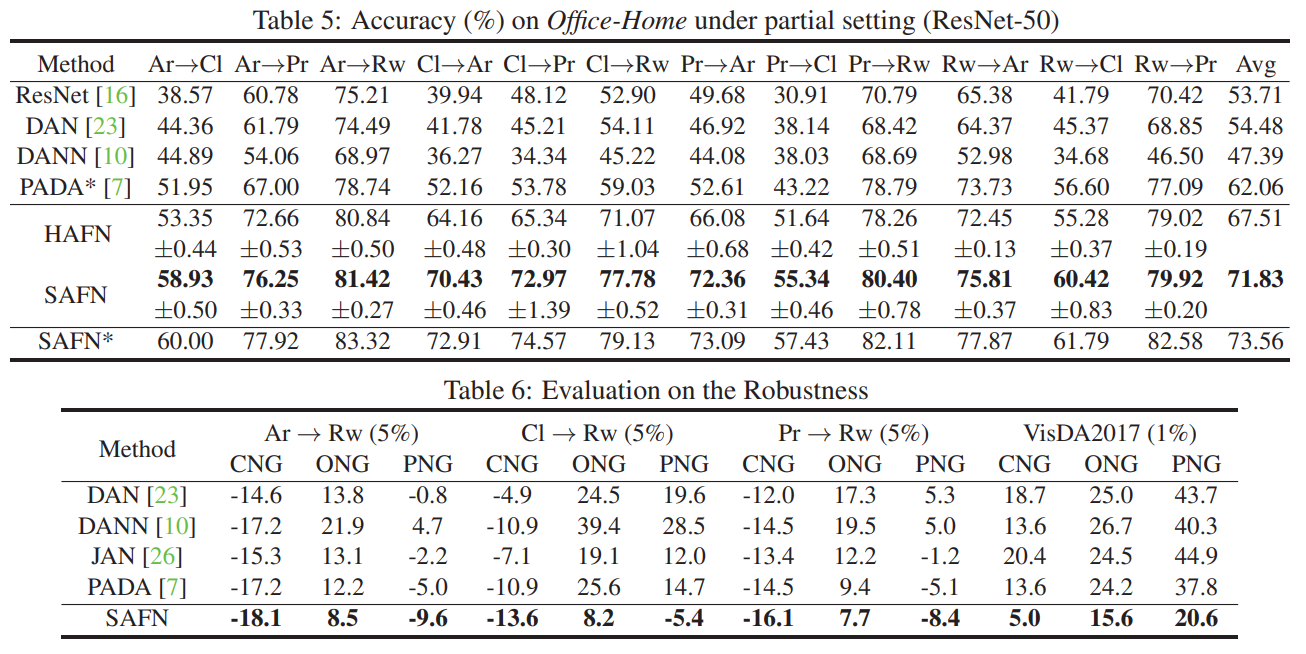
Experiment
Conclusion
We have presented an innovative discovery for UDA, revealing that the model degradation on the target domain mainly stems from its much smaller feature norms with respect to that of the source domain. To this end, we demonstrated that progressively adapting the feature norms of the two domains to a large range of values can result in significant transfer gains, implying that those task-specific features with larger norms are more transferable. Our method is parameter-free, easy to implement and performs stably. In addition, we successfully unify the computation of both standard and partial DA, and thorough evaluations revealed that our feature-norm-adaptive manner is more robust against the negative transfer. Extensive experimental results have validated the virtue of our proposed approach.